Finasteride Oral Tablet

Finasteride is an oral medication commonly used to treat male pattern baldness and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
It works by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, which converts testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that contributes to hair loss and prostate enlargement.
Finasteride is effective in slowing hair loss and promoting hair regrowth in many men.
But this drug is potent, and there may be some side effects and considerations you need to know about before starting treatment. But we’re here to help.
Today, we’ll explore everything you need to know about this drug.
We’ll talk you through how it works, what to expect during treatment, and pictures of patients before and after progress.
- What it is
- How it works
- Before and after
- Side effects
- How to reduce side effects
- Finasteride shedding
- Dosage
- Risks
- Interactions
- Safety
- Other factors to consider
- Alternatives
What is Finasteride?
Male pattern hair loss affects around 50% of men over the age of 50 in the UK.
It is one of the most common cosmetic conditions, and several treatments are available to help alleviate symptoms.
Finasteride is an oral tablet that treats conditions like androgenic alopecia and other male health problems.
It is a prescription-only medication for men; doctors will not recommend this to women or children because of harmful reactions and lack of research.
The drug comes in different branding, including Propecia and Proscar, but there are also generic versions that may be cheaper to buy.
Finasteride vs Propecia
Finasteride is the generic name of the active ingredient used in a medication that treats male pattern hair loss and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Propecia is a brand name specifically formulated to treat male pattern hair loss in men.
In essence, Propecia contains finasteride, but the drug is also available as a generic medication and under other brand names for different conditions, such as Proscar for BPH.
Both Propecia and Proscar, and their generic counterparts, are available by prescription. The main difference lies in their indicated use and dosage strength.

How does Finasteride for hair loss work?
Finasteride works by decreasing the levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in your body.
This is a hormone that plays an essential role in the development of “male” characteristics.
However, it can negatively affect normal hair follicle function by shrinking its size and leading to thinning hair.
DHT can also increase the size of the prostate and is negatively associated with prostate cancer.
By reducing the levels of DHT in your body, this drug may reduce hair shedding, combat male pattern baldness, and stimulate hair growth solely on your scalp.
How long does Finasteride take to work?
The drug has straightforward instructions that must be followed to achieve optimal Finasteride results.
We know from clinical trials that patients can show early signs of hair recovery after 3 to 4 months of continued use.
Early signs of recovery include minor regrowth in areas prone to hair thinning. You may also see a decrease in the number of hair strands falling out.
The full effects of Finasteride will appear some 6 to 9 months after starting treatment, as hair follicles need an extended time to reproduce new hairs.
Many people use this treatment as a preventative medication against hair loss. It can help stop it from developing in the first place rather than achieving regrowth.
Discuss your goals with your doctor to see if you can accomplish your goals with this route of treatment.
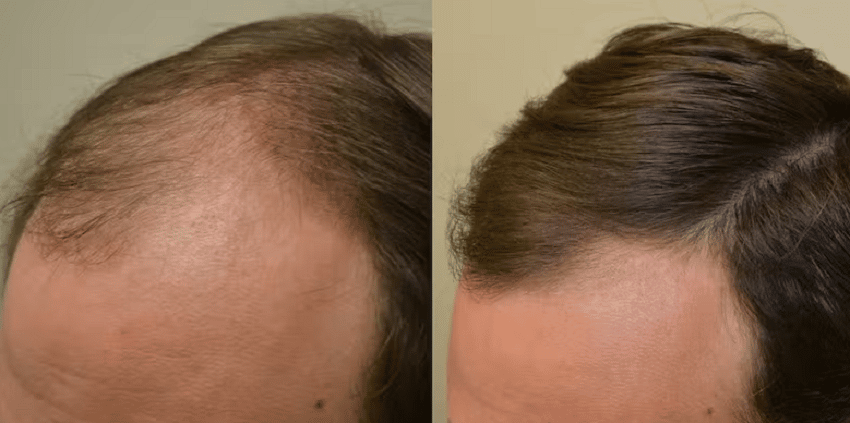
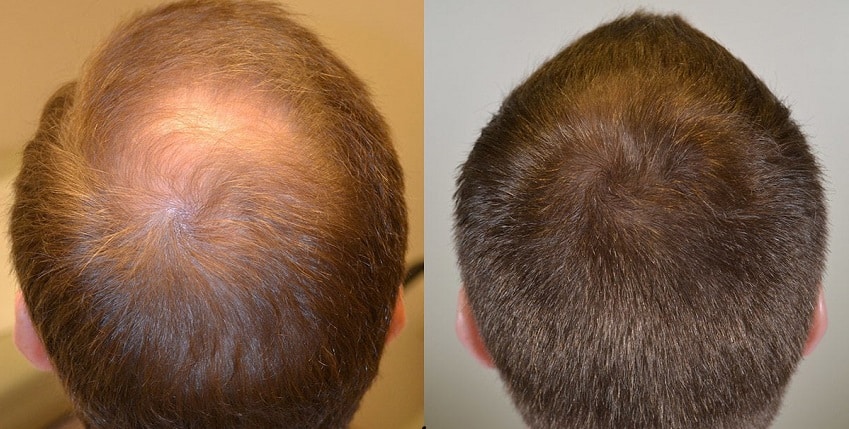
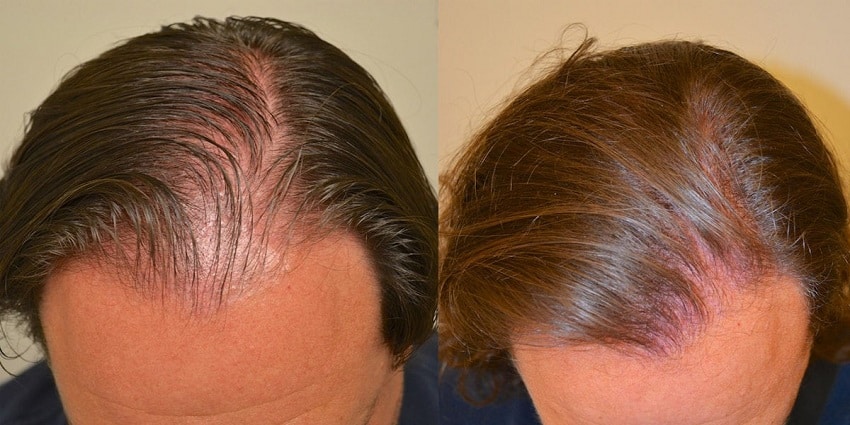
Finasteride before and after
As with any cosmetic treatment, no doubt you’re curious to see the firsthand results of using this course of treatment.
While every patient responds differently, the Finasteride before and after pictures will demonstrate the potential benefits of taking this medication.
Finasteride side effects: What to expect?
It’s essential to recognise that finasteride tablets for hair loss may cause potential side effects throughout treatment.
The most common, though, often pass without needing any medical attention.
Common side effects
Common side effects may fade within a couple of weeks, but if concerned at any point, you should talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
These include:
- A skin rash
- A decrease in sex drive
- Erectile dysfunction
- Ejaculation disorder
- Breast growth and tenderness
Serious side effects
There are more severe side effects, which you must take seriously. They have the potential to develop into even more severe conditions.
Contact your doctor or emergency services if you experience any of the following:
- Pain when urinating
- Blood in urine or semen
- Difficulty urinating
- Swollen tongue, throat, face, or lips
- An allergic reaction
- Depression
- Nipple discharge, lumps, or bumps may indicate male breast cancer
Please note: Drugs can affect everyone differently, and it is impossible to say conclusively that we’ve covered all potential side effects.
As with any medication, consult your doctor, who will be familiar with your medical history.
Only then can you make an informed decision on how this drug may affect you, interact with other drugs you are taking, and measure the risk of developing potential side effects.

How to reduce side effects of Finasteride
The appearance and severity of side effects can depend on the amount of medication you are taking. Here are some ways to reduce any side effects.
- Start with the lowest dose
Taking the lowest dose is one of the most effective ways of reducing side effects. If you still suffer side effects, there are other ways to alleviate symptoms. - Take your course of medicine before bedtime
Taking your medication at night time before bed may lessen your experience of side effects during the daytime. You can “sleep” them off. You can also decrease the severity by taking the tablet with food. - Eat a healthier diet
Certain foods may amplify side effects. Try to reduce fat in your diet, and focus on eating more vitamins and minerals to strengthen your body. Concentrate on increasing your uptake of fruits, vegetables, meat, and fish. - Reduce alcohol
Alcohol may increase dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in your body. DHT is a harmful hormone that shrinks hair follicles to such a degree that they cannot grow hair. DHT can also lessen the effect of certain medications. By reducing it, you’re eliminating this negative influence. - Avoid caffeine
Similar to alcohol, caffeine may increase DHT levels in your body, leading to more thinning and loss and reducing results from your course of medication. - Avoid extreme temperatures
Extreme heat (both hot and cold) can decrease the benefits of Finasteride. Avoid saunas, sun exposure, and extreme styling techniques such as hair straighteners or curling thongs. - Always follow the proper dosage
Only take the required amount; do not take any more, as this may inhibit your progress.
Finasteride shedding: What is it and what can you do about it?
Most patients experience a phenomenon known as Finasteride shedding, which usually presents itself soon after starting treatment.
Tablets stop the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase from converting testosterone into DHT, thus preventing harmful hormones from affecting hair follicles.
Any hair follicles already affected by DHT will move from the telogen phase (resting) into the active growth phase.
These hairs will fall out much earlier than anticipated – this is a normal occurrence, as their exit is making room for regrowth.
Hair shedding can return periodically after 3 to 6 months of treatment.
There are no ways to avoid this hair shedding – you should look at this as a good sign that the treatment is working.
What you can do is channel your energy into supporting and nurturing the new hair that is growing back.
Ensure you eat a varied diet full of vitamins and minerals, eliminate harmful junk, and keep your scalp well cared for.
Finasteride dosage
In order to achieve optimal Finasteride hair regrowth it’s essential to follow the proper dosage which may vary based on different factors. These include:
- The condition you are being treated for and its severity
- Your age
- Your intiial reaction
- Any other conditions you are suffering from or medications you’re taking
Below is a summary of typical dosages for patients.
Again, this list is not exhaustive, and there may be other plans you and your doctor may pursue.
Consult with them to find the appropriate dosage for your treatment.
Dosage to treat hair loss
- Generic treatment: Finasteride, 1 mg oral tablet
- Branded treatment: Propecia, 1 mg oral tablet
Dosage for adults (18+): 1 mg daily.
Children (younger than 18 years old): There is no established dosage for people below 18 years of age, and Finasteride is never prescribed for children.
Dosage to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia
- Generic treatment: Finasteride, 5 mg oral tablet
- Branded treatment: Proscar, 5 mg oral tablet
Dosage for adults (18+): 5 mg daily.
Children (younger than 18 years old): There is no established dosage for people below 18 years of age, and Finasteride is never prescribed for children.
Speak to your doctor before you start taking it to confirm the right dosage to treat your androgenetic alopecia.

What are the risks of taking Finasteride for hair growth?
As with any medication, there are some risks involved.
Please read the following when considering Finasteride for treating your thinning problems:
Fetus defect risk
If you’re pregnant or trying to conceive, avoid handling broken tablets. Any physical contact with this drug may cause defects in developing male fetuses.
Prostate cancer risk
Finasteride has been known to affect the prostate gland by reducing prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels.
Talk to your doctor if you have irregular PSA levels during your treatment.
Allergic reactions
This medication can trigger an allergic reaction in some people. Be on the lookout for the following symptoms:
- Swollen tongue or throat
- Developing hives
- Have trouble breathing
Seek emergency help and call 999 if you develop any of the above symptoms.
Furthermore, stop taking your dosage, as future reactions could be even more severe.
Skin contact
Avoid physical skin contact with this drug if you are currently pregnant or trying to conceive, as it can penetrate your skin and cause birth defects in the fetus.
Existing health conditions
You should be cautious of using this drug if you suffer from the following:
Liver disease
Finastatre is processed in the liver, and your body may take longer to process it if you suffer from liver disease.
It may build up in your system over time, and you might suffer possible side effects.
A possible solution for this may be to receive a lower dosage.
Prostate cancer
In men, the drug affects the prostate and may increase the risk of developing irregular forms of cancer or make it grow faster.
Who else should avoid taking Finasteride?
- Pregnant & breastfeeding women should avoid this drug, as it can negatively affect child development.
- Additionally, there is no research on whether the drug is safe or effective in treating children.
Can Finasteride interfere with other drugs?
Yes, it can interact with prescription and nonprescription medications, including stopping one or both drugs from working as intended.
Known drug interactions include carbamazepine, rifampin, itraconazole, and erythromycin.
Inform your doctor of any medications you take, including hair growth products, herbs or supplements, or hair growth vitamins.
They can help you understand the drug’s potential risks.
Taking Finasteride safely
Always take your tablets as instructed by your doctor and pharmacist.
Read the instructions and drug information label thoroughly before using it, and consult them if you have any questions or are taking other medication simultaneously.
Additionally, you may ask your doctor regarding topical Finasteride, as this form is thought to have lower risks overall.
However, you must keep in mind the differences in efficacy when it comes to topical vs oral finasteride.
5 key factors to consider before you take Finasteride
If taking this drug to treat male pattern hair loss, keep the following in mind:
- General safety
Only take this drug as directed by your doctor and pharmacist.
Do not cut, chew or crush tablets. Stop taking them immediately if you develop any severe reactions. - Storage
Ensure you keep this medication at room temperature, between 15°C to 30°C, and it is out of direct sunlight.
Avoid keeping this medication in any room prone to moisture, for example, the bathroom. - Refilling Finasteride prescriptions
Your doctor will include a specified number of refills when writing your initial prescription. - Traveling with Finasteride
The x-ray machine at an airport will not damage your medication in this instance. You may be required to present your pharmacy label to an official.
For that reason, it’s highly recommended that you keep your tablets in your carry-on luggage.
If driving in a car, avoid storing them in places with extreme heat, for example, in the glove compartment. - Monitoring the effects of Finasteride
It’s important to track how your body is reacting to treatment.
One of the most important things to monitor is your PSA levels, which can be used to monitor prostate cancer.
Your doctor will help explain any of your concerns relating to this. They may also discuss other hair restoration options for you to consider.
What other hair loss treatments are available?
A hair transplant offers a permanent solution to your haircare woes.
With just a straightforward procedure, you can change your entire hairline and treat any thinning areas around your scalp.
Moreover, the procedure is so cutting-edge that techniques like the FUE2 have a success rate of up to 90-95%.
Hair transplants are incredibly straightforward – a highly skilled surgeon will extract hair follicles from donor areas and strategically place them into thinning or bald spots.
The result? Hair growth like you’ve never experienced before!
However, if you’re reluctant to undergo surgery another treatment option is a similar drug known as Dutasteride.
Finasteride vs Dutasteride
Dutasteride is a common alternative as both medications inhibit the action of the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, which converts testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
While both drugs inhibit the 5-alpha-reductase enzyme, Finasteride primarily blocks one type (Type II) of this enzyme, whereas dutasteride blocks both major types (Type I and Type II).
This means that Dutasteride can reduce DHT levels more than Finasteride, which is why it’s often prescribed off-label to treat hair loss.
However, its main use is the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Both medications have similar side effects, including potential sexual side effects like decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and ejaculatory disorders.
However, because Dutasteride has a more potent DHT-lowering effect, there might be a slightly higher risk of experiencing these side effects.
While both medications can provide temporary results, only a hair transplant is capable of giving a final solution to hair loss that will last for a lifetime.
FAQ
Below are some common questions many patients have when beginning their treatment:
Yes, it’s effective in treating male pattern hair loss and benign prostatic hyperplasia. For hair loss, it can slow progression and promote regrowth in many men. However, individual results may vary, and there are potential side effects to consider.
Taking more than recommended may lead to potentially serious side effects. This drug can cause erectile dysfunction and skin irritation among other issues. Only follow your doctor’s directions on dosage, and if you experience severe symptoms, seek medical attention.
Some studies have shown that it can temporarily reduce sperm count in some men. The reduction is generally reversible upon discontinuation of the medication. However, it’s important to consult with a physician if fertility is a concern while taking it.
Taking finasteride can lead to a modest increase in circulating testosterone levels. It works by inhibiting the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) through its action on the 5-alpha-reductase enzyme. As a result, while DHT levels decrease, there can be a slight rise in testosterone levels, typically in the range of 5-10%.
You are not strictly required to take it after a hair transplant. However, many surgeons recommend it to help maintain the non-transplanted hair and prevent further hair loss. Taking finasteride can help stabilize this hair loss and support the overall results of the transplant.
Yes, while some surgeons may recommend Finasteride after a hair transplant it is by no means necessary. It’s up to the patient to decide whether the risks are worth the potential results based on his individual situation.
No, it does not lower testosterone. In fact, it can lead to a modest increase in circulating testosterone levels as discussed above.
After stopping, its half-life is approximately 4-7 hours in young adults and up to 8 hours in elderly individuals. However, its effects on DHT suppression can last longer, and it may take several days to weeks for DHT levels to return to baseline.
Yes, a man can take finasteride while his wife is pregnant. However, there are precautions to be aware of. Pregnant women, especially those expecting a male baby, should not handle crushed or broken tablets because of the potential risk of causing abnormalities in the fetus.
Last medically reviewed on June 27th, 2025
- Kaufman KD et al. Finasteride in the treatment of men with androgenetic alopecia. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 1998;39(4):578-589.https://doi.org/10.1016/S0190-9622(98)70007-6
- Irwig MS. Persistent Sexual Side Effects of Finasteride: Could They Be Permanent? The Journal of Sexual Medicine. 2012;9(11):2927-2932.https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1743-6109.2012.02846.x
- Finasteride — finasteride tablet, coated. (2019).https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=ecd2fbb2-a4bd-44f2-831d-179e7dbf0741
- Proscar — finasteride tablet, film coated. (2021).https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=7c01f541-1c88-400c-41a9-7cbb9dee50c0
- Propecia — finasteride tablet, film coated. (2021).https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=4e07adb4-7807-47d3-b9a9-2332a3047410
- Zito PM, Bistas KG, Syed K. Finasteride.2021.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513329/