Hair Transplant Methods: FUT, FUE & DHI

There are various techniques available to address different types and degrees of hair loss.
Each technique has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, which are essential to understand ahead of making your decision.
By exploring these techniques, you can gain valuable insights into the procedures involved, recovery times, potential risks, and expected outcomes.
Let’s dive into the world of hair transplant techniques to help you navigate this transformative journey effectively.
How does hair transplantation work?
Hair transplants work by moving individual hair follicles from the ‘donor site’ to a bald or balding part known as the ‘recipient site’.
It is primarily used to treat male pattern baldness, as the transplanted hairs are genetically resistant to balding.
There are two main methods of harvesting hair follicles, strip harvesting (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE).
After the cosmetic surgery, the scalp may be very tender, and the patient may need to take medications for pain, swelling, and possible antibiotics to prevent infection.
The transplanted hair will fall out after a few weeks, but new growth will start to appear after a few months.
The success of hair transplantation depends on the skill of the surgeon, as well as the quality of the donor hair.
When done successfully, the transplanted hair will grow in the natural growth pattern, providing a permanent solution to hair loss.
Hair transplant methods
There are three different hair transplantation techniques used in treating thinning hair, FUE, FUT and DHI.
Hair transplants work by taking healthy follicles from the back or sides of the head and transplanting them into the balding areas.
1. FUE hair transplant
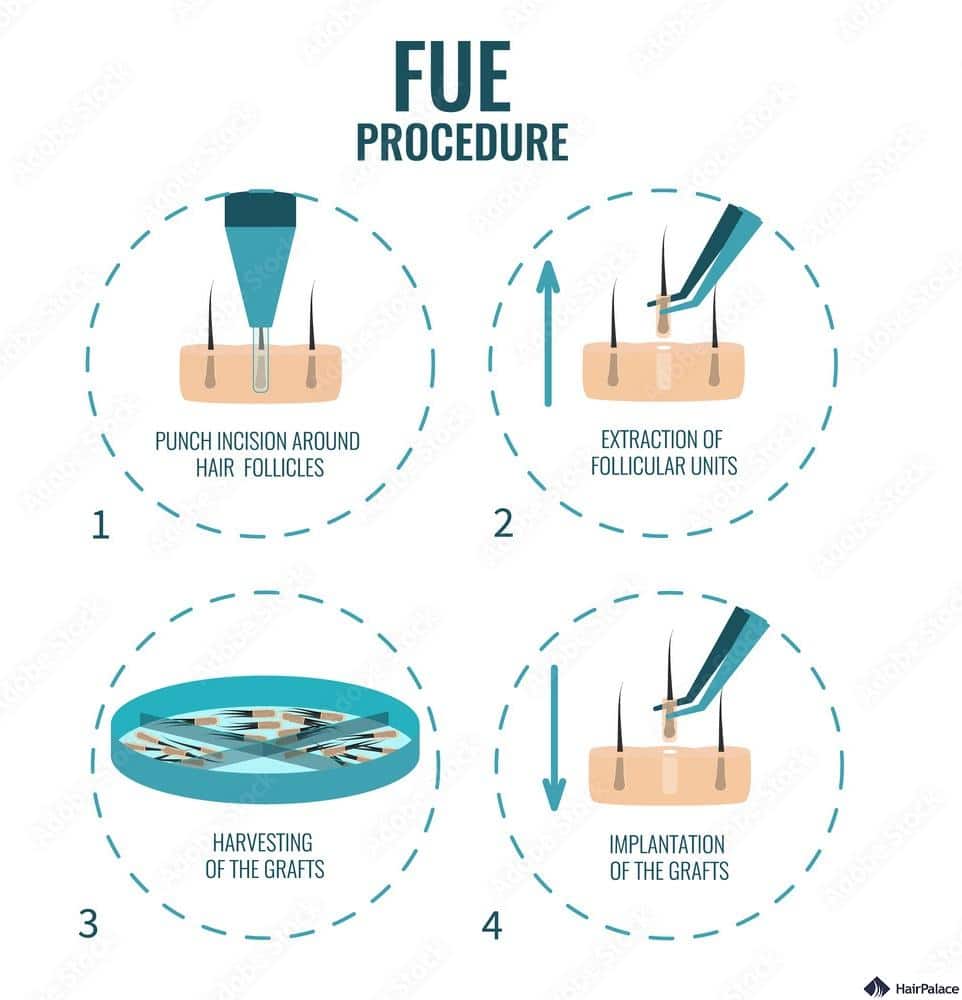
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is a hair transplant technique where the follicular units are extracted individually.
Hairs are taken from the donor site using a micropunch tool.
FUE is less invasive than FUT, resulting in a quicker recovery time and less post-operative discomfort.
FUE hair transplants also avoid the linear scar associated with FUT.
This makes it a preferred choice for patients who want to wear their hair short after the hair replacement surgery.
The procedure is time-consuming and can be more costly than FUT.
Yet its precision and minimal scarring make it a highly sought-after method for hair restoration.
2. DHI hair transplant
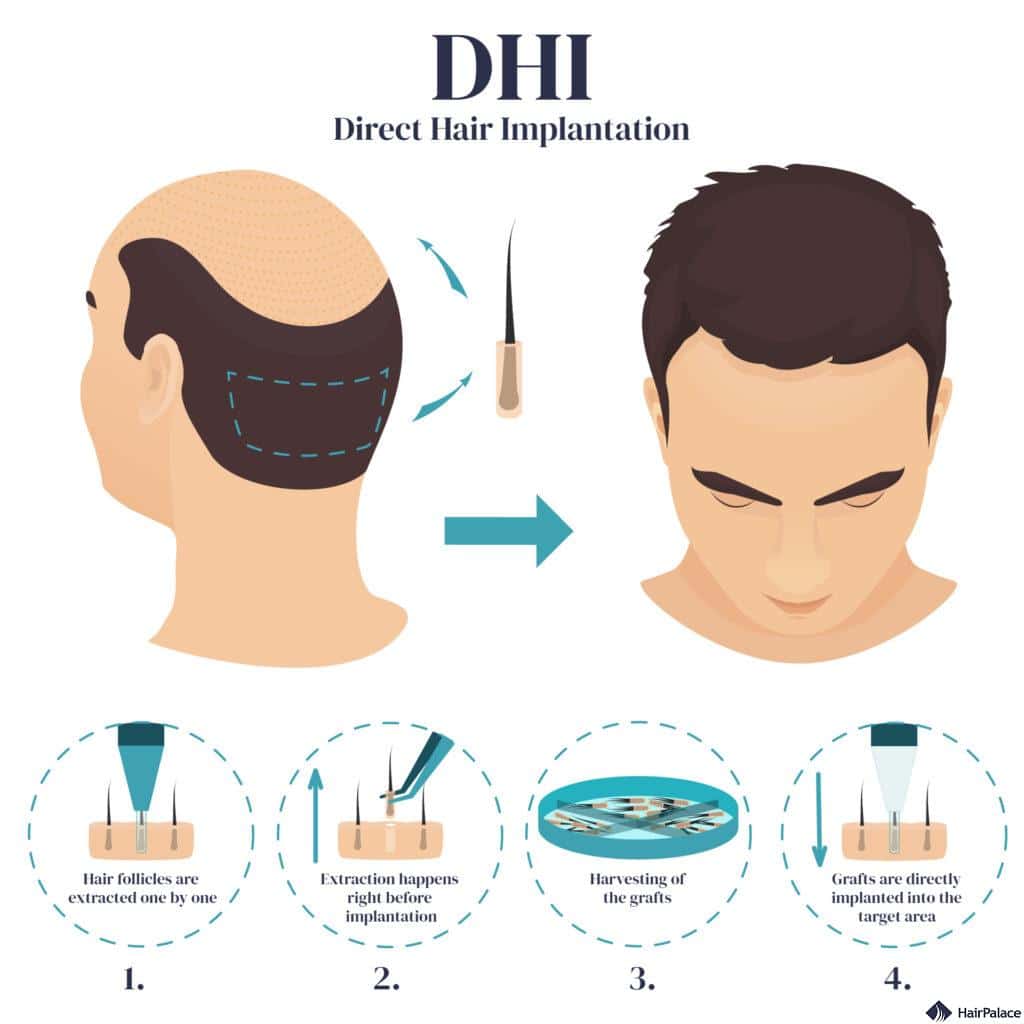
Direct Hair Implantation (DHI) is a hair transplant technique which eliminates the need for creating incisions before implantation.
The hair transplant surgeon uses a tool called the Choi implanter pen which allows for the immediate implantation of grafts at the desired angle and depth.
However, the extraction part is done with the FUE technique.
With DHI there is no need to create incisions beforehand, which is said to result in less scarring and quicker healing.
On the other hand, DHI is the most expensive method of transplanting hair out of the three.
While this technique may sound promising initially, there is little factual evidence to suggest that it offers any significant advantages over standard FUE hair restoration surgery.
3. FUT hair transplant
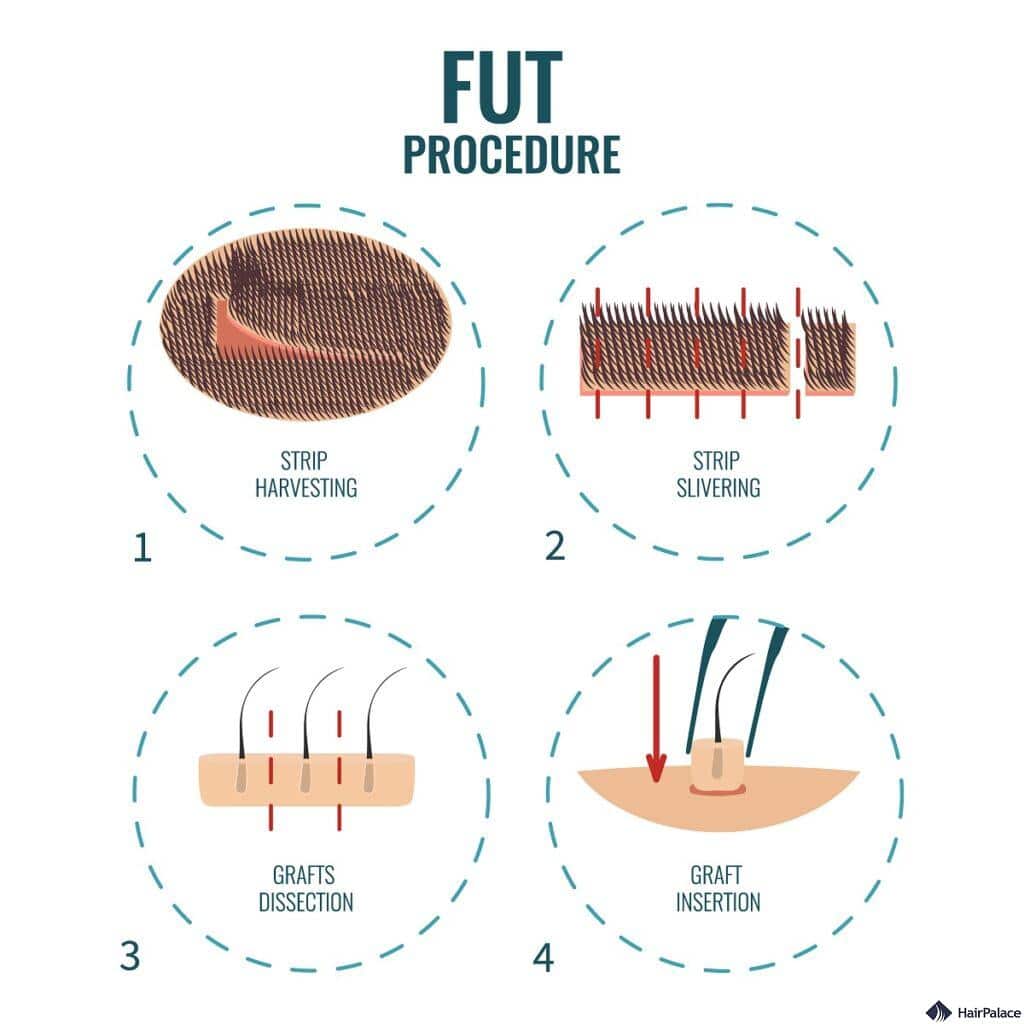
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) is a type of hair transplant technique that involves removing a strip of hair-bearing scalp from the donor area.
This way of carrying out hair transplant surgery is also referred to as the strip method.
FUT offers several advantages that make it suitable for individuals with extensive hair loss.
One significant advantage is its high graft survival rate.
This ensures that transplanted hairs have a good chance of taking root and growing successfully.
Additionally, FUT allows for larger quantities of grafts to be transplanted in a single session.
This makes it ideal for those with extensive hair loss history. However, FUT does come with some disadvantages to consider.
The most notable drawback is the presence of a linear scar resulting from the removal of the donor strip.
FUT also requires a longer recovery time compared to FUE due to the nature of the incision and sutures involved.
4. Trivellini method
The Trivellini hair transplant method, also known as the Mamba Instrument or Trivellini System.
This method represents an advanced evolution in follicular unit extraction (FUE) techniques.
This system utilizes a unique multi-phasic and programmable extraction device that allows for customized settings tailored to individual patient’s needs.
It offers enhanced precision in follicle extraction, reduces trauma to the donor area, and can potentially improve the survival rate of transplanted hair follicles.
The Trivellini method is particularly noted for its ability to adapt to different types of hair and skin, making it the most versatile option in the field of hair transplant surgeries.
5. Artas hair transplant
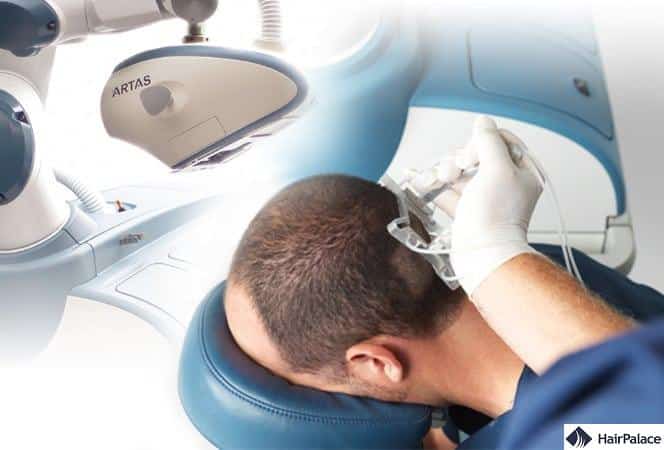
The ARTAS hair transplant method is a robotic hair restoration procedure that uses advanced digital imaging and precision robotics to enhance the follicular unit extraction (FUE) technique.
This system scans the scalp to identify and select the best donor hairs for transplantation with great accuracy and speed, minimizing damage to existing hair.
The robotic arm then extracts follicular units with precision and implants them into the recipient areas.
The ARTAS method is known for its high level of consistency, reduced human error, minimal scarring, and quicker recovery times compared to manual FUE methods.
It’s especially suitable for patients seeking a minimally invasive, technologically advanced solution to restore hair density.
6. Neograft hair transplant
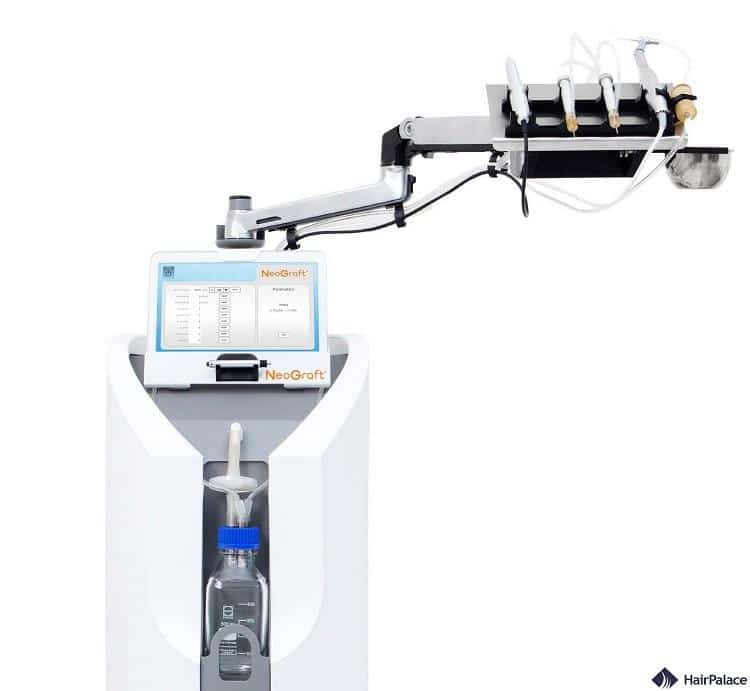

The NeoGraft hair transplant method is an automated version of the Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) technique.
It utilizes a specialized device to remove hair follicles from the donor area of the scalp and then implant them in balding areas.
This method is known for being less invasive than traditional strip harvesting, as it doesn’t require any stitches or leave a linear scar.
NeoGraft is praised for its efficiency in harvesting hair follicles, reducing the time of the procedure and potentially improving the survival rate of the transplanted hair.
Additionally, it offers a quicker recovery time and is suitable for patients who prefer a less invasive approach with natural-looking results.
Alternatives to hair transplant methods
There are several popular treatments to choose from if you feel like hair transplantation isn’t right for you.
1. IPRF
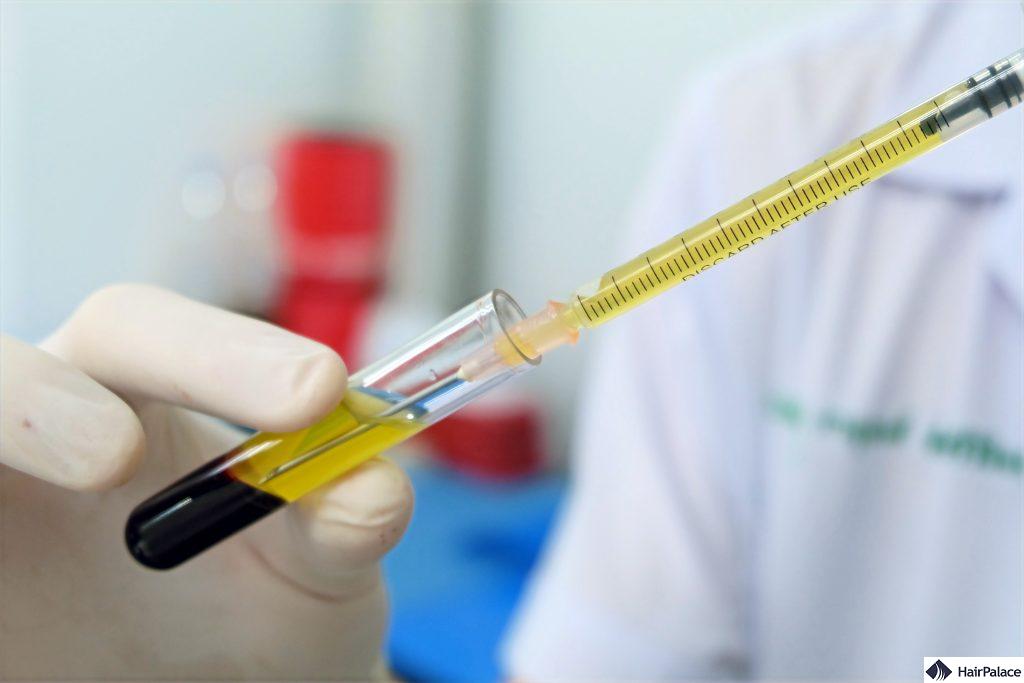
Injectable Platelet Rich Fibrin (IPRF) is a treatment for hair loss that involves using the patient’s blood to stimulate hair growth.
This process includes drawing a small amount of blood from the patient.
The blood is then spun in a centrifuge to separate the fibrin and platelet-rich plasma (PRP).
Unlike traditional PRP treatments, IPRF doesn’t require the addition of anticoagulants; it maintains more white blood cells and circulating stem cells.
When injected into the scalp, IPRF releases growth factors slowly over time, promoting natural healing and rejuvenation.
This can lead to the stimulation of hair follicles, potentially resulting in thicker and healthier hair growth. altogether, this tends to lead to a more natural hairline.
IPRF is considered a natural and minimally invasive treatment option for various types of hair loss, It’s often used in conjunction with other hair restoration procedures to enhance results.
2. PRP
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy is a treatment used to combat hair loss by harnessing the body’s healing abilities.
The process involves drawing a small amount of the patient’s blood.
This is then centrifuged to separate the plasma enriched with platelets.
These platelets are key components in the body’s natural healing process and are rich in growth factors.
When this concentrated plasma is injected into the scalp, it stimulates the hair follicles.
This potentially encourages new hair growth and strengthens existing hair.
The success of PRP therapy can vary, and multiple sessions are often required for optimal results.
3. Stem cell treatment
Stem cell treatment for hair loss is an emerging and promising area in regenerative medicine, aimed at restoring hair growth by revitalizing dormant hair follicles.
This treatment involves harvesting stem cells from the patient’s own body.
Often from fat or other tissues—and then processing these cells to concentrate them.
These concentrated stem cells are then injected into the scalp where hair loss has occurred.
The theory behind stem cell therapy is that these cells can encourage the growth of new hair follicles or rejuvenate existing ones that have become inactive, leading to hair regrowth.
This treatment is considered a cutting-edge approach to hair restoration.
It has the potential to provide more natural and long-lasting results compared to traditional methods.
However, it’s important to note that stem cell therapy for hair loss is still in the experimental stages.
While early results are promising, more research is needed to fully understand its effectiveness, optimal protocols, and long-term outcomes.
4. Hyperbaric oxygen chamber
So how does a hyperbaric oxygen chamber work?
A hyperbaric oxygen chamber allows you to breathe pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber.
This treatment is primarily known for its use in decompression sickness, serious infections, and wounds that won’t heal due to diabetes or radiation injury.
In theory, this treatment enables the patient’s lung to gather more oxygen than would normally be possible.
The increased oxygen can boost oxygen levels in the blood, which can aid cell repair and various body functions.
Hyperbaric oxygen chamber benefits include an increase in the supply of oxygen and collagen, reduced inflammation and better stem cell mobilization.
While its use against hair loss is not widely studied, due to its various benefits it’s also believed to support thicker hair growth.
Implementation fields of hair transplant methods
Eyebrow implants

Eyebrow transplants are a cosmetic procedure designed to restore or enhance the appearance of the eyebrows.
This procedure is similar to scalp hair transplant surgery, typically using the FUE technique.
The goal is to recreate or thicken the eyebrows in a shape that suits the patient’s facial features.
Each hair follicle is implanted individually, allowing for precise control over the eyebrow’s shape, density, and direction of hair growth.
Beard implants

Beard implants, also known as a beard transplant, are a cosmetic procedure designed to enhance the density and appearance of a man’s beard.
This procedure is similar to hair transplants on the scalp and is often sought by men who have sparse, patchy, or non-existent beard hair due to genetics, scarring, or medical conditions.
The process is done similarly to Follicular Unit Extraction hair transplants.
The surgeon carefully places each graft to match the natural growth direction and pattern of the beard.
The transplanted hair grows like natural beard hair and can be shaved or styled as desired.
Recovery time is relatively short, with most patients resuming normal activities within a few days.
The latest technology of hair transplant
Stem cell hair transplant surgery or hair cloning is the most exciting new method on the market.
Hair cloning

Hair cloning is an experimental technique aimed at treating hair loss.
The concept involves taking cells from a person’s existing hair follicles and replicating them in a lab (cloning).
The surgeons are then re-implanting these cloned cells into the scalp to grow new hair follicles which will in turn create new hairs.
The process typically starts with the extraction of dermal papilla cells or other stem cells from the hair follicle.
These cells are responsible for hair growth and are cultured in a lab to multiply.
The newly produced cells are then injected back into the scalp’s balding areas.
Cells are expected to form new hair follicles and produce hair.
Hair cloning holds great promise as it could potentially provide an unlimited source of new hair for individuals experiencing hair loss.
Last medically reviewed on May 31st, 2024
- ISHRS: 2020 Practice Census Resultshttps://ishrs.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/Report-2020-ISHRS-Practice-Census-05-22-20.pdf
- Kanti V, Messenger A, Dobos G, et al. Evidence-based (S3) guideline for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia in women and in men - short version. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32(1):11-22.https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.14624
- Vogel James E et al. Hair Restoration Surgery: The State of the Art. Aesthetic Surgery Journal 2013;1:33http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1090820X12468314
- Zito PM, Raggio BS. Hair Transplantation. Updated 2021https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547740/


