Zinc for Hair Growth: Is it effective?

Hair loss is a concern that affects millions of people worldwide, and while genetics, stress, and hormonal imbalances often take the blame, nutrient deficiencies are frequently overlooked.
Among the key nutrients linked to healthy hair, zinc is vital in maintaining scalp health, supporting hair follicle function, and regulating hormones that influence shedding and regrowth.
But what is the exact relationship between zinc and hair health?
In this article, we’ll explore the science behind zinc’s role in hair health, what happens when you don’t get enough, and whether supplementation could make a meaningful difference in your hair care routine.
- What is zinc?
- Is zinc good for hair growth?
- Combining zinc with other vitamins
- Zinc rich foods for hair growth
What is zinc?

Zinc is an essential mineral that your body needs for numerous functions, including immune support, wound healing, and cell growth.
It also plays a vital role in maintaining healthy skin, hair, and nails. Since the body doesn’t store zinc, it must be obtained regularly through diet or supplements.
Is zinc good for hair growth?

Zinc plays a multifaceted role in promoting hair growth and maintaining scalp health.
Hair follicles are among the fastest-growing cells in the body. Zinc supports the active division of cells in the hair follicle matrix, which is essential for producing strong, healthy hair strands.
It helps balance hormone levels, including androgens like DHT (dihydrotestosterone), which, when elevated, can shrink hair follicles and lead to thinning hair.
Zinc also regulates the sebaceous glands, which produce oil (sebum) on the scalp.
Balanced oil production keeps the scalp moisturised and prevents issues like dandruff and clogged follicles that can aid hair loss.
Zinc has anti-inflammatory effects that can help calm scalp conditions such as seborrheic dermatitis or psoriasis. It also protects cells from oxidative stress, which can damage hair follicles over time.
Suppose you suffer from scalp irritation or microtrauma (e.g., from scratching, harsh styling, or treatments like microneedling).
In that case, zinc supports faster healing, reducing the risk of scarring that could cause hair loss.
Zinc benefits for hair
Let’s quickly summarise the multiple effects zinc has on your hair:
- Aids cell division and growth
- Regulates hormones
- Contributes to sebum production
- Has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties
- Wound healing effects
How much zinc for hair growth?
For hair growth, the recommended daily zinc intake is:
- Men: 11 mg per day
- Women: 8 mg per day
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women: 11–12 mg per day
If you’re taking zinc specifically for hair health, short-term zinc supplementation in the range of 15–30 mg per day is often recommended.
This dosage may help address a deficiency or support regrowth during shedding phases like telogen effluvium.
Combining zinc with other vitamins
Zinc supplements alone are often not enough to bring significant change.
If you want to maximise the effects of zinc for hair loss, combining zinc with other hair loss treatments and vitamins is often the best approach.
Zinc and selenium for hair growth

Using zinc and selenium together can be a powerful strategy for promoting hair growth and maintaining a healthy scalp.
Selenium, a vital trace mineral and antioxidant, plays several key roles in hair regrowth.
It supports the production of glutathione peroxidase, an enzyme that protects hair follicle cells from oxidative stress.
Selenium also regulates thyroid function (which is essential for healthy hair cycle dynamics) and aids in detoxifying the body from harmful substances.
A selenium deficiency can lead to dry, brittle hair and, in severe cases, hair loss.
When combined with zinc, which helps regulate oil production, supports cell regeneration, and controls DHT levels.
This makes it an effective natural remedy for both female pattern hair loss and male pattern baldness.
The two nutrients complement each other’s antioxidant effects, strengthen immune system function, and enhance thyroid health.
However, it’s important to avoid excessive intake of selenium, as doses above 400 mcg per day can be toxic.
Zinc and copper for hair growth

While zinc is widely recognised for its role in hair follicle repair, oil regulation, and hormonal balance, it must be carefully balanced with copper, especially during supplementation.
Copper plays a vital role in melanin production, helping to maintain natural hair colour and prevent premature greying.
It also contributes to collagen and elastin synthesis, which support the scalp’s structural integrity and blood flow, as well as the cross-linking of keratin, the key protein in hair strands.
Additionally, copper is essential for proper iron metabolism, which indirectly ensures an adequate oxygen supply to hair follicles.
However, excessive zinc intake can deplete copper levels, potentially leading to deficiencies that may result in anaemia or even hair thinning.
For this reason, many high-quality hair growth supplements include both minerals in a carefully balanced ratio to ensure optimal hair and scalp health.
Zinc and iodine for hair growth

Iodine is crucial for the production of thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism and directly influence the hair growth cycle.
Adequate iodine levels help ensure that hair follicles remain in the anagen (growth) phase longer and support overall cellular energy, which benefits optimal hair health.
When iodine is deficient, it can lead to hypothyroidism, a common cause of hair thinning, dry scalp, and even loss of eyebrow hair.
Zinc complements iodine’s effects by aiding in the conversion of inactive thyroid hormone (T4) into its active form (T3).
Without sufficient zinc, this conversion is impaired, even if iodine levels are adequate, resulting in diminished thyroid function.
Conversely, without iodine, the thyroid cannot produce hormones at all.
Nutritional deficiencies in either mineral can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to increased shedding and slower regrowth.
Zinc and magnesium for hair growth
Magnesium, while often overlooked in treating hair loss, is involved in over 300 enzymatic processes that indirectly affect hair health.
It supports protein synthesis, including keratin production, improves blood circulation to nourish hair follicles, and regulates calcium levels to prevent buildup on the scalp that can clog follicles.
Additionally, magnesium enhances the absorption of other nutrients, including zinc.
A magnesium deficiency may lead to scalp tension, poor nutrient delivery, and stress-induced hair loss.
When taken together, magnesium and zinc tablets for hair growth support optimal nutrient absorption, hormonal balance, reduced stress levels, and healthy hair growth.
This is why they are often combined in supplements, such as ZMA (zinc, magnesium, and vitamin B6).
These are typically marketed for sleep and muscle recovery, and can also benefit hair health through improved metabolic and hormonal function.
Biotin and zinc for hair growth

Among the most widely recognised nutrients for supporting hair growth and maintaining scalp health are biotin and zinc, often combined in supplements for their complementary benefits.
As a water-soluble B-vitamin, biotin plays a vital role in keratin production and supports cellular energy metabolism, helping to fuel the rapid turnover of cells within the hair follicles.
It also helps reduce hair brittleness and improves strand thickness and strength.
Although rare, biotin deficiency can lead to symptoms such as hair thinning, scalp flaking, and even loss of eyebrow or eyelash hair.
Supplementation is especially common among individuals recovering from stress, illness, or hormonal fluctuations to enhance hair health.
Zinc supplementation, on the other hand, protects and optimises the environment in which hair grows by regulating hormones, supporting the immune system, and maintaining a healthy, balanced scalp.
Together, biotin and zinc provide a holistic approach to optimal hair growth.
Biotin strengthens the structure and texture of the hair, while zinc ensures the conditions are right for growth.
Moreover, zinc enhances the body’s ability to effectively use biotin, making their combination particularly beneficial for preventing shedding and promoting stronger, healthier hair.
Zinc rich foods for hair growth
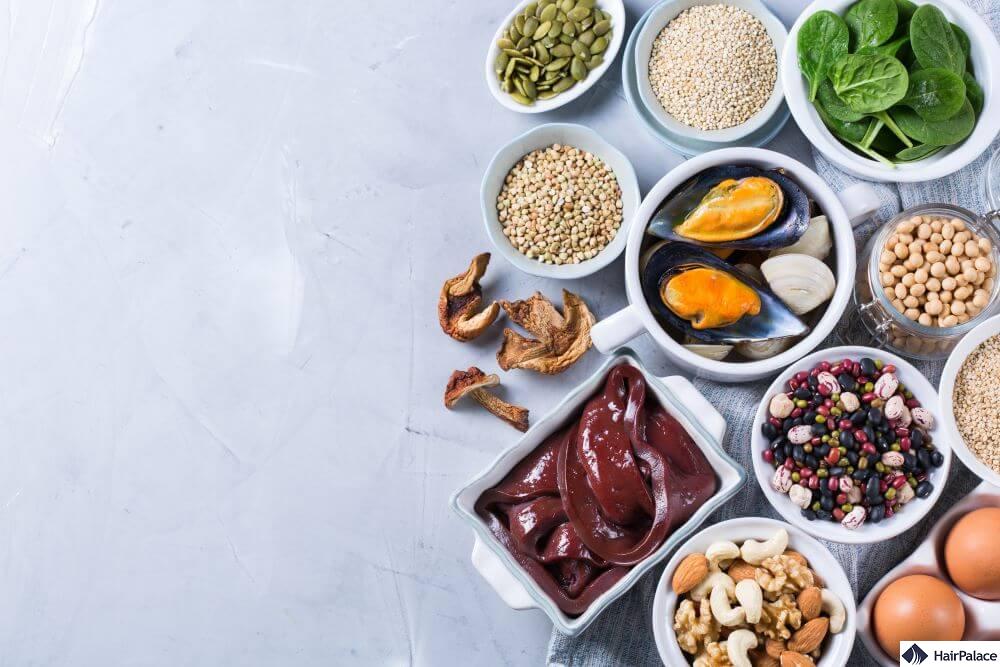

Here are some of the best zinc-rich foods that support hair growth by nourishing hair follicles, regulating hormones, and maintaining a healthy scalp:
- Oysters: One of the richest natural sources of zinc
- Beef: Especially lean cuts like sirloin or chuck roast
- Lamb: Another excellent source with high zinc content
- Chicken (dark meat): Contains more zinc than white meat
- Pork: Especially pork shoulder or loin
- Eggs: Contain modest amounts of zinc and protein
- Dairy: Provide zinc in an easily absorbed form
- Pumpkin seeds: A top plant-based source of zinc
- Hemp seeds: Also rich in healthy fats and zinc
- Chickpeas: Great in salads, hummus, or curries
- Lentils: Good source of plant-based protein and zinc
- Quinoa: Nutrient-dense whole grain with moderate zinc
- Cashews: A zinc-rich snack that supports hair and skin health
- Tofu: It contains zinc and is a solid choice for vegetarians
FAQ
For hair growth, the recommended daily intake of zinc is around 8 mg for women and 11 mg for men. However, doses between 15–30 mg daily are sometimes used short-term for hair loss, under medical supervision. Excessive zinc (over 40 mg/day) can cause side effects and should be avoided long-term.
It can be beneficial for hair loss, especially if the cause is a zinc deficiency. It plays a role in hair follicle function, cell growth, and repair. However, excessive zinc intake may disrupt the balance of other minerals and worsen hair loss, so proper dosing is important.
Last medically reviewed on August 29th, 2025
- NIH State-of-the-Science Panel. National Institutes of Health state-of-the-science conference statement: multivitamin/mineral supplements and chronic disease prevention. Am J Clin Nutr 2007;85:257S-264Shttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17209206?dopt=Abstract
- Almohanna HM, Ahmed AA, Tsatalis JP, Tosti A. The Role of Vitamins and Minerals in Hair Loss: A Review. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2019 Mar;9(1):51-70. doi: 10.1007/s13555-018-0278-6. Epub 2018 Dec 13. PMID: 30547302; PMCID: PMC6380979.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30547302/
- Wang R, Lin J, Liu Q, Wu W, Wu J, Liu X. Micronutrients and Androgenetic Alopecia: A Systematic Review. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2024 Nov;68(22):e2400652. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202400652. Epub 2024 Oct 23. PMID: 39440586.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39440586/
- Chiu CH, Huang SH, Wang HM. A Review: Hair Health, Concerns of Shampoo Ingredients and Scalp Nourishing Treatments. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2015;16(12):1045-52. doi: 10.2174/1389201016666150817094447. PMID: 26278532.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26278532/


