Stemoxydine for Hair Loss

Hair loss affects millions worldwide, often impacting self-confidence and quality of life.
Many individuals seek gentler, non-hormonal alternatives for hair growth, even though pharmaceutical treatments like minoxidil and finasteride remain widely used.
One such option gaining attention in the cosmetic dermatology world is Stemoxydine, a patented topical molecule developed by L’Oréal.
Brands market Stemoxydine as a scalp-activating ingredient that combats hair thinning and increases hair density without causing the systemic side effects linked to traditional medications.
This article explores how Stemoxydine works, its benefits, potential drawbacks, and how it compares to other hair loss treatments.
- What is Stemoxydine?
- How Stemoxydine works for hair loss
- What are the benefits of using Stemoxydine for hair loss?
- Stemoxydine side effects
- Stemoxydine vs. Minoxidil
- Stemoxydine vs. Finasteride
- Stemoxydine before and after
- Is Stemoxydine a good solution for hair loss?
- How to apply Stemoxydine
- Stemoxydine alternatives
What is Stemoxydine?
Stemoxydine is a patented cosmetic molecule that L’Oréal developed to reduce hair thinning and support hair density recovery.
Manufacturers most commonly include it in topical hair products designed for people experiencing hair loss or thinning.
It creates a low-oxygen (hypoxic) environment in the scalp, which researchers believe stimulates dormant hair follicles and encourages them to re-enter the growth (anagen) phase.
How Stemoxydine works for hair loss

Hair follicles can enter a “sleep” phase (telogen) where they stop producing hair.
In people experiencing hair thinning, more follicles stay dormant instead of cycling back into the growth phase.
Stemoxydine creates a chemical environment that mimics low oxygen levels. This is important because stem cells in hair follicles are naturally activated in low-oxygen conditions.
By simulating this environment, Stemoxydine is believed to “wake up” dormant follicles, pushing them back into the growth phase.
Clinical data and L’Oreal research suggest that it may lead to a potential increase in the number of hairs in the anagen (growth) phase after a few months of use.
However, these effects are cosmetic, not medical, so they might help mild to moderate thinning, but not treat the underlying causes of baldness.
Additionally, these positive results only last as long as you use Stemoxydine on an ongoing basis.
What are the benefits of using Stemoxydine for hair loss?

Using Stemoxydine against hair loss offers several benefits:
Increases hair density
Clinical studies (mostly by L’Oréal) show that consistent use of Stemoxydine can lead to a 3–4% improvement in visible hair density over three months.
Lightweight and easy to apply
Stemoxydine is typically found in non-greasy topical serums or lotions. This makes it easy to integrate into a daily routine without altering your hairstyle.
Non-hormonal formula
Unlike finasteride, Stemoxydine is a non-hormonal molecule. This means that there are no systemic side effects, and it’s ideal for both sexes.
Can support other hair loss treatments
It can be used alongside minoxidil or microneedling to combat thinning hair and enhance overall hair regrowth efforts, especially for people with diffuse thinning.
Reactivates dormant hair follicles
Stemoxydine mimics a low-oxygen environment, which helps wake up dormant follicles and push them back into the active growth (anagen) phase of the hair growth cycle.
Stemoxydine side effects
It is generally well-tolerated, especially when compared to pharmaceutical options like finasteride or minoxidil.
However, some users may experience mild scalp irritation, such as redness, itchiness, or a slight burning sensation, particularly those with sensitive skin.
Occasional dryness or flakiness can also occur, especially with alcohol-based formulations.
In rare cases, allergic reactions or contact dermatitis may develop due to other ingredients in the product.
Unlike other hair loss treatments, Stemoxydine does not affect hormone levels or blood pressure and does not enter the bloodstream, making it safe for both men and women.
Some users might notice initial hair shedding as follicles transition into the growth phase, but this is typically temporary.
Stemoxydine vs. Minoxidil

Stemoxydine and minoxidil are both topical treatments used to combat hair loss, but they differ significantly in their mechanisms and effects on hair growth biology.
Minoxidil is an FDA-approved pharmaceutical treatment with decades of clinical research supporting its effectiveness.
It acts as a vasodilator, improving blood flow to hair follicles, which increases hair growth.
Minoxidil is more potent than Stemoxydine, often producing visible regrowth in 4–6 months, especially in cases of androgenetic alopecia.
However, it may cause more noticeable side effects such as initial hair shedding, scalp irritation, and, in rare cases, systemic effects like dizziness or heart palpitations due to absorption.
While both treatments are available in topical forms and suitable for men and women, minoxidil is generally recommended for more advanced hair loss.
Stemoxydine vs. Finasteride

Unlike Finasteride, Stemoxydine is suitable for both men and women, and it’s typically well-tolerated, only causing minimal side effects.
Finasteride, by contrast, is a prescription oral medication and a systemic treatment.
It works by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the hormone primarily responsible for male pattern baldness.
By lowering DHT levels, finasteride can significantly slow hair loss and even promote regrowth, especially at the crown and mid-scalp.
It is clinically proven and FDA-approved, but only for use in men.
Finasteride’s effectiveness often surpasses that of cosmetic solutions like Stemoxydine, but it comes with a risk of hormonal side effects.
These may include reduced libido, erectile dysfunction, and mood changes in a small percentage of users.
Stemoxydine before and after
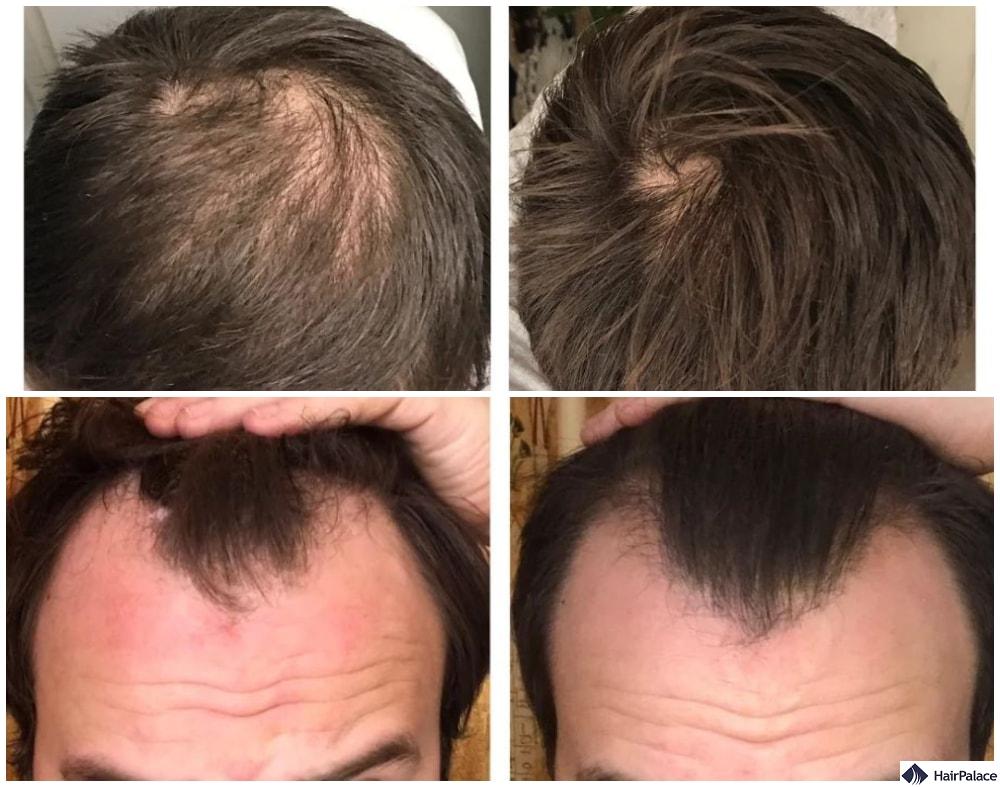
Is Stemoxydine a good solution for hair loss?
Stemoxydine can be a suitable option for addressing hair loss, particularly if you’re in the early stages of thinning or experiencing diffuse shedding.
It’s ideal for those who prefer a non-hormonal, topical solution with minimal side effects and are looking for a gentler alternative to treatments like finasteride or minoxidil.
Additionally, it can be a useful complement to other therapies such as microneedling or minoxidil.
However, if you have advanced androgenetic alopecia with significant hairline recession or bald spots, or if you’re expecting dramatic regrowth, Stemoxydine may not be sufficient.
How to apply Stemoxydine
To apply hair serum for thinning hair, start by using it on clean, dry hair. Avoid applying it after using styling products.
Most serums, such as Vichy Dercos or La Roche-Posay Kerium, recommend a daily dose of 1 ml (about one full dropper or 10–12 pumps).
Part your hair in sections and distribute the serum evenly across thinning areas, focusing on zones like the crown, top, or temples, rather than just on the hair itself.
Gently massage the product into your scalp for 1–2 minutes using your fingertips to promote absorption and boost circulation.
Allow the serum to fully absorb and do not rinse it out.
For best results, apply it once daily at the same time each day, and expect stemoxydine results after at least three months of consistent use.
Stemoxydine alternatives
If Stemoxydine fails to provide long-term relief, there are several other treatment options to help you promote hair growth.
- Minoxidil: Increases blood flow to hair follicles, clinically proven, visible results in 3–6 months.
- Finasteride: Blocks DHT production, highly effective for crown and mid-scalp regrowth.
- Redensyl: Stimulates hair stem cell activity; promotes follicle renewal. Early studies show promising results, often used in serums
- Natural DHT Blockers: May reduce DHT activity, mild to moderate support for hair retention
- Microneedling: Induces minor injury to promote healing and growth factor release; improves absorption of topical treatments like minoxidil or Stemoxydine
- Peptide Serums: Support follicle health, strengthen hair, and reduce inflammation. Mild to moderate thinning; combination with other treatments.
- Oral Presentations. Int J Trichology. 2014 Jul-Sep;6(3):113–39. PMCID: PMC4158624.https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4158624/
- Park BS, Kim WS, Choi JS, Kim HK, Won JH, Ohkubo F, Fukuoka H. Hair growth stimulated by conditioned medium of adipose-derived stem cells is enhanced by hypoxia: evidence of increased growth factor secretion. Biomed Res. 2010 Feb;31(1):27-34. doi: 10.2220/biomedres.31.27. PMID: 20203417.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20203417/
- Jeon SH, Kim H, Sung JH. Hypoxia enhances the hair growth-promoting effects of embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells via NADPH oxidase 4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Mar;159:114303. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114303. Epub 2023 Jan 25. PMID: 36706635.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36706635/
- Shapiro J. Safety of Topical Minoxidil Solution: A One-Year, Prospective, Observational Study. Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery. 2003;7: 322-329.https://doi.org/10.1007/s10227-002-0121-6
- Messender AG, Rundegren J. Minoxidil: mechanisms of action on hair growth. British Journal of Dermatology. 2004150(2):186-194.https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.05785.x
- Kaufman KD et al. Finasteride in the treatment of men with androgenetic alopecia. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 1998;39(4):578-589.https://doi.org/10.1016/S0190-9622(98)70007-6


